Only YOU Can Prevent Type 2!
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a lifelong health condition that affects how your body uses food for energy. In people who have diabetes, the body can’t produce any or enough of a hormone called insulin, which allows the body to use sugar for energy. When the body can’t use the sugar found in our blood for energy, it builds up, leading to greater health issues like vision loss and kidney disease.
The causes of diabetes vary depending on the type, but the need for glucose monitoring and treatment is universal for those affected with any variation of the disease. While there is not currently a cure for diabetes, many people are able to live long and healthy lives by closely monitoring their blood glucose levels and adopting healthier lifestyles.
Diabetes in Kentucky
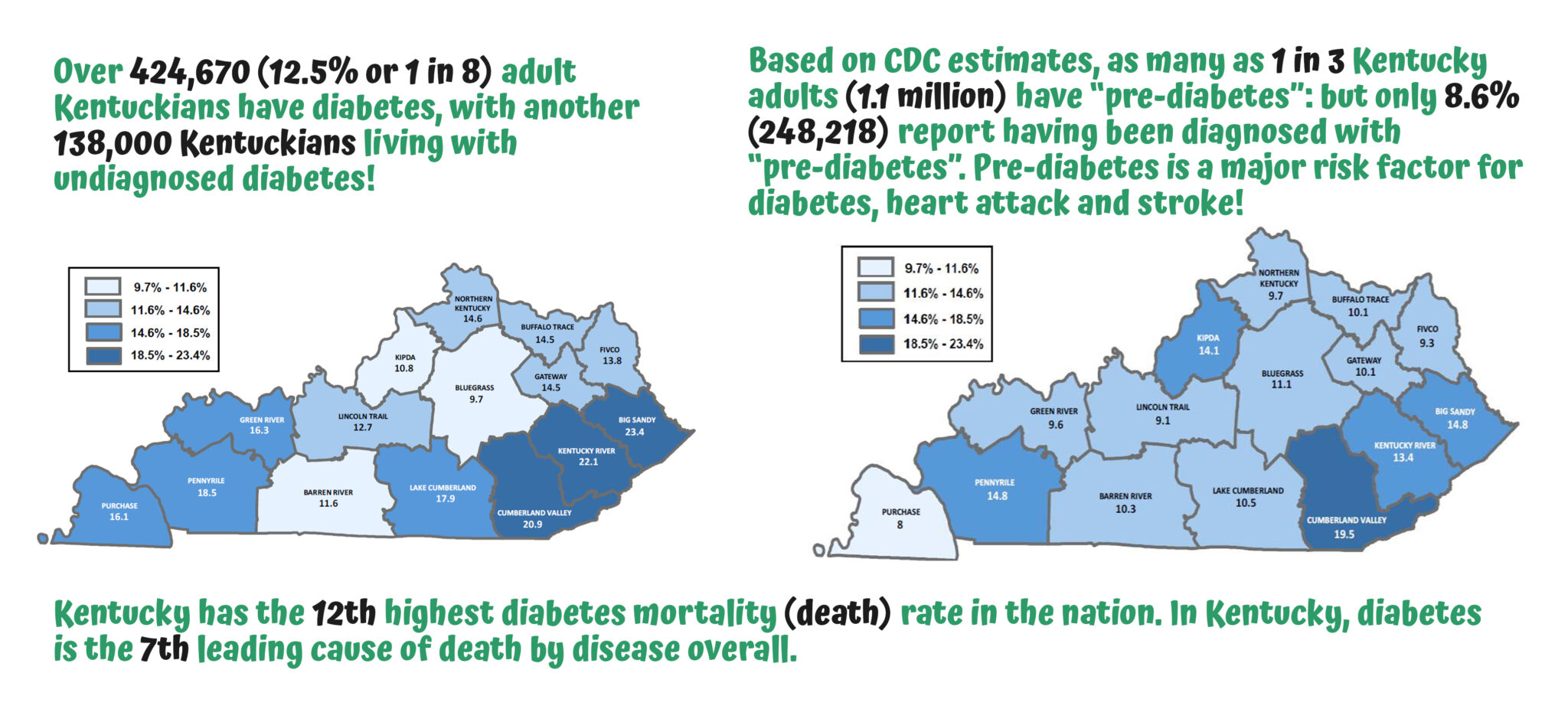
Prediabetes
What Is Prediabetes?
Prediabetes is a health condition in which the person’s blood sugar levels are above normal, but not high enough to be considered a type 2 diabetic. Around 96 million Americans have prediabetes, and around 80% of those don’t know that they have it. Prediabetes is a serious condition as it raises risk for heart disease, stroke, and developing type 2 diabetes; however, with healthy lifestyle changes, prediabetes can be reversed.
- Risk Factors:
- Overweight
- 45 or older
- Have an immediate relative with type 2 diabetes
- Are physically active less than 3 times a week
- Have had gestational diabetes or given birth to a baby weighing more than 9 pounds
- Are African American, Latino or Hispanic, or Indigenous American.
Types of Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes
- Type 1 diabetes is thought to be caused by the body’s immune system attacking itself by mistake. In this case, the immune system harms the body’s ability to produce insulin. Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in children, teens, and young adults. Symptoms develop quickly, and individuals with type 1 diabetes must take insulin daily in order to survive. Those suffering from type 1 diabetes make up 5-10% of the diabetic population. If you suspect you or your child have type 1 diabetes, please make an appointment with your primary care provider as soon as possible.
- Risk factors:
- Family history (having an immediate family member with type 1 diabetes
- Age (usually develops in children, teens, and young adults)
- Ethnic background: caucasian people are more likely to develop type 1 diabetes.
- Symptoms:
- Urinate (pee) a lot, often at night
- Are very thirsty
- Lose weight without trying
- Are very hungry
- Have blurry vision
- Have numb or tingling hands or feet
- Feel very tired
- Have very dry skin
- Have sores that heal slowly
- Have more infections than usual
- Have nausea, vomiting, or stomach pains.
Type 2 Diabetes
- Type 2 diabetes is a health problem that develops over time and is typically diagnosed in adults, although the number of children, teens, and young adults receiving diagnoses is increasing every day. With type 2 diabetes, the body still produces insulin, but is unable to keep blood sugar at normal, healthy levels. Around 90-95% of individuals with diabetes have type 2 diabetes. Unlike type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes can be prevented with healthy lifestyle changes. People with type 2 diabetes may not experience any symptoms, so it is important to understand the risk factors and have your blood sugar tested at routine checkups.
- Risk factors:
- Have prediabetes
- Overweight
- 45 years or older
- Have an immediate family member with type 2 diabetes
- Are physically active less than 3 times a week
- Have had gestational diabetes or given birth to a baby weighing more than 9 pounds
- Are African American, Latino or Hispanic, or Indigenous American.
Gestational Diabetes
- Gestational diabetes is a health condition that only develops in pregnant women, and typically goes away after giving birth. This condition places the developing baby at risk for health problems and at a higher risk of developing obesity in childhood. Having gestational diabetes also puts both mother and child at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. Gestational diabetes may not cause any symptoms, so it is important to know the risk factors and have your OBGYN test you between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy.
- Risk factors:
- Had gestational diabetes during a previous pregnancy
- Have given birth to a baby that weighed more than 9 pounds at birth
- Are overweight
- Are over 25
- Have a family history of type 2 diabetes
- Have polycystic ovary syndrome
- Are African American, Latino or Hispanic, Pacific Islander or Indigenous American
Managing Diabetes
Glucose Monitoring
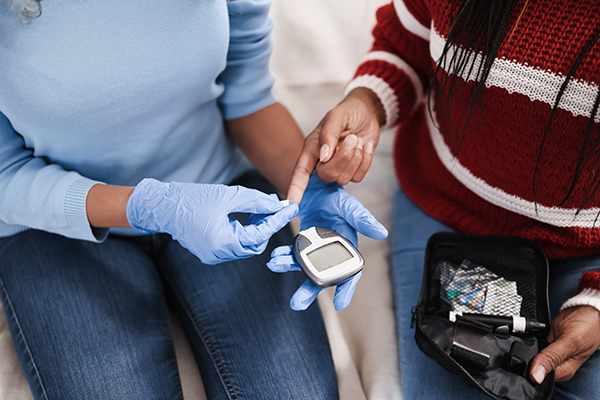

The most important aspect of diabetes management is keeping a steady blood glucose level. When glucose levels are elevated, that’s when problems start to occur. The longer high blood glucose levels go untreated, the more damage they can cause. So the first order of business is keeping a close eye on your levels.
Diet
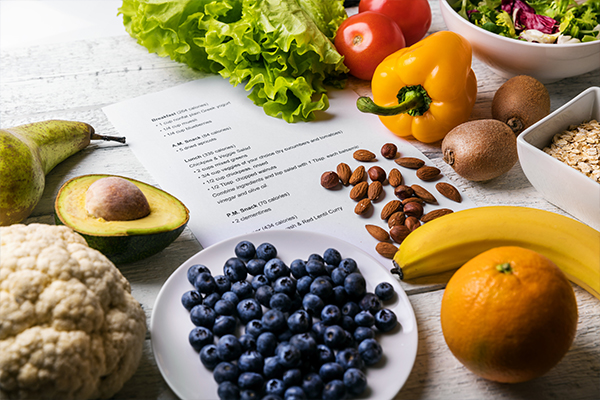

Having a well-balanced diet is critical to proper diabetes management. It’s also how those who have been diagnosed with prediabetes can help to mitigate and even prevent it from developing into type 2 diabetes, for which there is no cure.
The most important factors in a balanced diet are:
- Monitoring carbohydrate intake! Carbohydrates are what affect blood glucose levels the most, and those with insulin dependent diabetes need to know precisely how many carbohydrates you will have at meal time to adjust for the amount of insulin they would take to offset it. Limiting carb intake is also just a good baseline for a healthy diet.
- Portion control! Just like your carb intake, it’s important to consider the portion size for all meals, being sure to keep your plate balanced with a mixture of starches, fruits and vegetables, proteins, and fats.
- Avoid sugary beverages! Sugary beverages such as sweet tea and sodas are high on calories and carbohydrates and offer little, if any, nutrition to your diet. They also cause your blood sugar to spike quickly, so it’s best to avoid them in general, and especially for those who’ve been diagnosed with any form of diabetes.
Exercise
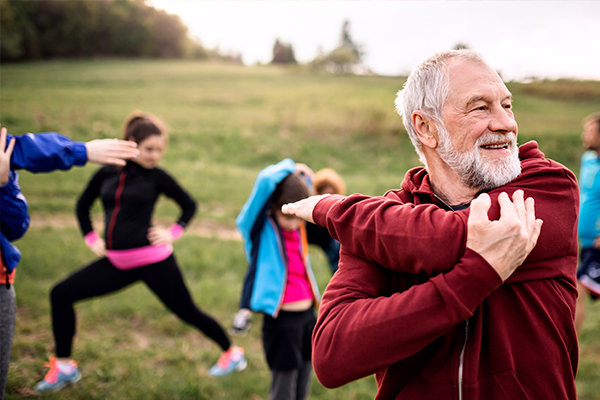

Physical activity and exercise play an extremely important role in diabetes management. When you exercise, insulin sensitivity is increased, so your muscle cells are better able to use any available insulin to take up glucose during and after activity. This is how exercise can help lower blood sugar in the short term.
The more strenuous your workout, the longer the effect lasts. But don’t think you have to hit the gym to be effective! Even light activities such as walking, housework, gardening, or just generally being on your feet for extended periods of time can improve your blood sugar.
If you’d like to know more about how diet can affect diabetes, or where to find more information about healthy eating and living, contact us today and set up a consultation!
Diabetes Education: What You Need To Know
- Prediabetes classes/education
- 1 on 1 education for prediabetic people
- Information about newly diagnosed diabetics
- Glucose monitoring
Diabetes Support/Living Well Support Groups
Get Help With Diabetes
For More Information Contact:
Kelly Dawes RN, BSN, CDCES, MLDE
Pennyrile District Health Department
KellyR.Dawes@ky.gov
(270) 522-8121 Ext: 212
Fax: (270) 522-5384
Caldwell County Health Center
270-365-6571
Crittenden County Health Center
270-965-5215
Livingston County Health Center
270-928-2193
Lyon County Health Center
270-388-9763
Trigg County Health Center
270-522-8121 Ext. 212